Enterprises' IT expenditure, 2021
Software is enterprises’ largest IT-related expense
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2023-02-02 8.00
In 2021, enterprises’ IT expenditure was SEK 215.7 billion, and software expenditure accounted for almost half of total IT expenditure. This is shown by data from Enterprises’ IT expenditure survey.
IT expenditure increases with the size of enterprises, measured as the number of employees. This applies both to total expenditure and to each type of IT expense. The largest enterprises account for 67.6 percent of total IT expenditure, small enterprises 12.3 percent and medium-sized enterprises 20.1 percent.
| 10–49 employees | 50–249 employees | 250+ employees | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer equipment | 3 379 | 4 132 | 8 734 | 16 245 |
| Telecommunication equipment | 1 119 | 1 341 | 5 228 | 7 689 |
| Leasing of computer and telecommunication equipment | 1 353 | 1 608 | 4 737 | 7 699 |
| Consulting expenditure for software development or improvement | 5 859 | 10 254 | 31 595 | 47 709 |
| Software purchases | 7 111 | 12 731 | 39 604 | 59 445 |
| ICT services | 7 777 | 13 206 | 55 939 | 76 922 |
| Total | 26 599 | 43 271 | 145 838 | 215 708 |
Enterprises’ expenditure for software
In this year’s survey, enterprises’ software expenditure is divided into two areas:
- consulting expenditure for software development or improvement
- software purchases.
This means that previous years’ statistics on software expenditure are not comparable with this year’s figures.
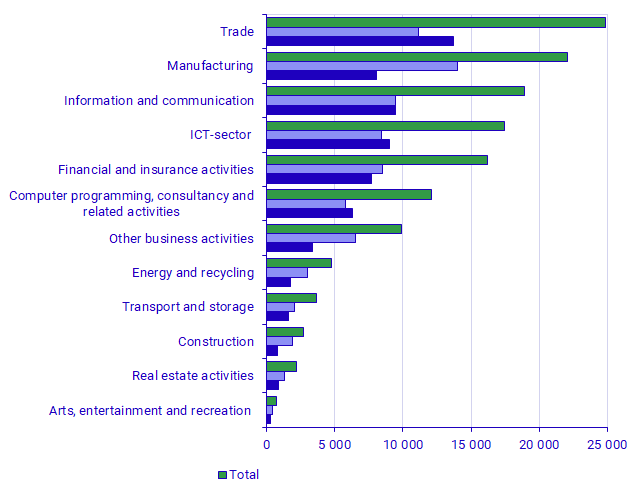
By industry, Trade accounts for the highest expenditure for software, at SEK 24.8 billion. Next comes Manufacturing, accounting for SEK 22.0 billion, then Information and communication at SEK 18.9 billion.
The ICT-sector, which is a subset of several industries, accounts for SEK 17.5 billion. Computer programming, consultancy and related activities, which is part of Information and communication, represents SEK 12.1 billion. As a percentage, Computer programming, consultancy and related activities contributes 63.8 percent of the total expenditure on software in the Information and communication industry.
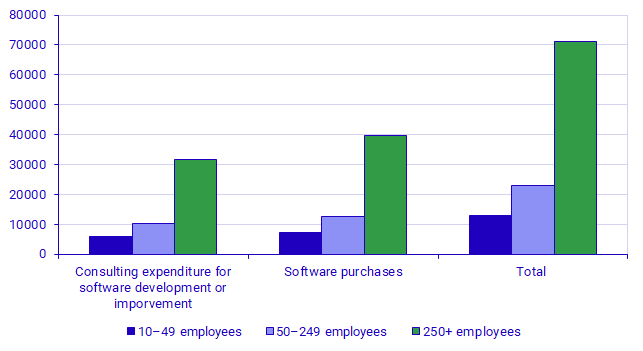
Broken down by size class, the largest enterprises accounted for 66.4 percent of total expenditure and investments in software in 2021, equalling SEK 71.2 billion.
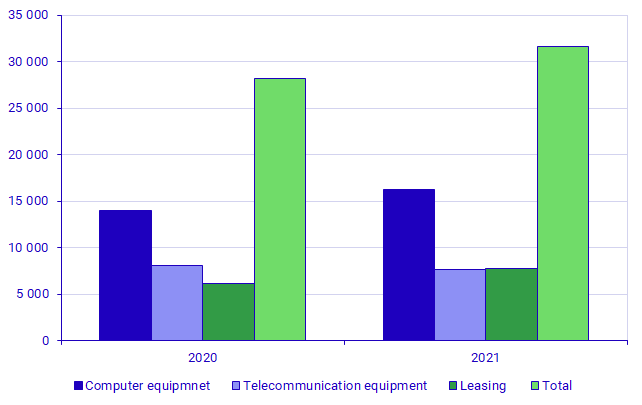
Enterprises’ expenditure on hardware is increasing
Enterprises’ total hardware expenditure has increased by SEK 3.5 billion, from SEK 28.1 billion in 2020 to SEK 31.6 billion in 2021, which represents a percentage change of 12.4 percent – in current prices.
The following diagram shows that divided into computer equipment, telecommunication equipment and leasing, expenditure on leasing hardware has increased most. This expenditure has increased from SEK 6.1 billion to SEK 7.7 billion, equalling a percentage change of 26.2 percent. Then comes expenditure on computer equipment, which has increased from SEK 14.0 billion in 2020 to SEK 16.2 billion in 2021, a percentage change of 16.2 percent. By contrast, expenditure on telecommunication equipment has fallen from SEK 8.0 billion in 2020 to SEK 7.7 billion in 2021, equalling a percentage change of -4.5 percent.
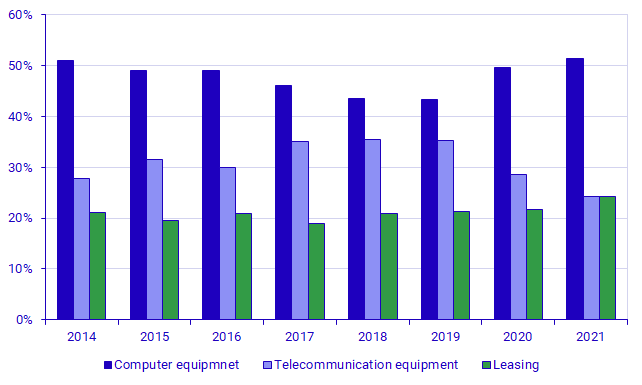
The following diagram shows the expenditure for each type of hardware expressed as shares of total hardware expenditure. A clear change over time is that leasing expenditure has increased since 2017, while expenditure on telecommunication equipment has declined. The change between 2020 and 2021 means that this is the first year since the start of the time series that leasing expenditure has reached the level of telecommunication equipment expenditure.
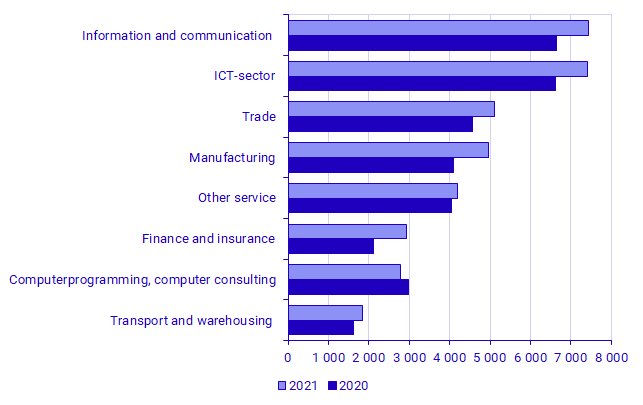
Hardware expenditure varies between industries
Expenditure on hardware rose between 2020 and 2021 in all of the industries below, except in Computer programming, consultancy and related activities – in current prices.
The selected industries below are the largest industries in terms of hardware expenditure. The highest change as a percentage is in Financial and insurance activities at 39.5 percent, while the lowest is in Other service enterprises at 3.4 percent. Computer programming, consultancy and related activities shows a 6.6 percent decline.
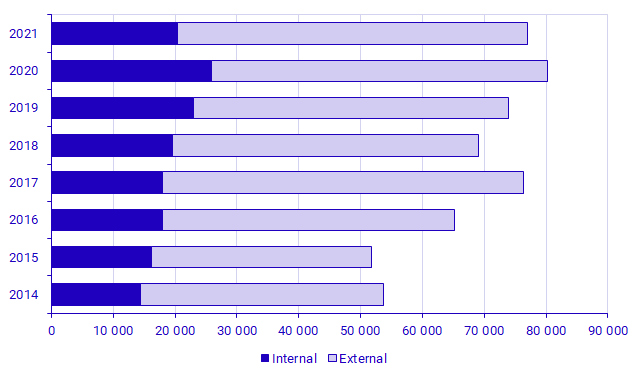
Enterprises’ expenditure on purchasing IT services is declining
This year’s survey shows that enterprises’ expenditure on IT services in 2021 was SEK 76.9 billion, which is a decrease of SEK 3.3 billion, or -4.1 percent, compared with 2020 – in current prices. Purchases from external suppliers are the most common, making up 73.4 percent of total expenditure on IT services. Compared with 2020, purchases from external suppliers have risen by 3.9 percent, while purchases from internal suppliers have decreased by 21.0 percent.
From 2020 there is a shift in expenditure from purchases from internal service providers to external ones. Many of the enterprises in the survey that previously purchased substantial amounts of IT services within their group have instead purchased them from external suppliers in 2021. At the same time the size of enterprises’ expenditure has increased. This is the main reason why purchases from internal suppliers are falling and purchases from external suppliers are on the rise despite a general drop in purchases of IT services.
Please note:
Ahead of this year’s survey, changes were made to the questionnaire, which causes a break in the time series for the questions concerning software expenditure. This means that previous years’ statistics on software expenditure are not comparable with this year’s figures.
Definitions and explanations
More information on the statistics, as well as results for other study domains, can be obtained from the Statistical Database on Statistics Sweden’s website.
Computer equipment: Computers, servers, monitors, projectors, scanners, printers, etc.
Telecommunication equipment: Phones, switchboards, burglar alarms, routers, etc.
Operating (rental) leases: resemble a normal rental situation. The enterprise rent the equipment of the lessor company for a fee. The lessor company bears the cost of service, maintenance, and insurance.
Finance leases: The financial risks and benefits associated with the ownership of equipment are essentially transferred from the lessor company to the enterprise.
Consulting expenditure for software development or improvement: An external party has developed new software or new functionality for existing software for the enterprises’ computer and telecommunication equipment, as well as machinery and other devices.
Software purchases: Expenditure for purchases of software for computer and telecommunication equipment and for machinery and other devices. These purchases include standard software or programs, including licences and plug-ins.
IT services: The enterprises purchase IT functionality without a need to invest in IT equipment. This may include service, maintenance, operation, cloud services, etc.
SNI – Swedish Industrial Classification Standard
The survey reports the following operations according to SNI 2007:
Mines and quarries – SNI 05–09
Manufacturing – SNI 10–33
Energy and recycling – SNI 35–39
Construction – SNI 41–43
Trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles – SNI 45–47
Transport and storage – SNI 49–53
Accommodation and food service activities – SNI 55–56
Information and communication – SNI 58–63
Computer programming, computer consulting and related activities – SNI 62
Financial and insurance activities – SNI 64–66 (subset; 64.19, 64.92, 65.1, 65.2)
Real estate activities – SNI 68
Other service enterprises – SNI 69–82
Arts, entertainment and recreation – SNI 90–93
Repair of computers and communication equipment – SNI 95.1
ICT-sector – SNI 26.1–26.4, 26.8, 46.5, 58.2, 61–62, 63.1, 95.1
For more information, see Swedish Standard Industrial Classification (SNI).
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
