Research and development in Sweden 2022
Research and Development in Sweden 2022
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2023-10-26 8.00
In 2022, research and development (R&D) expenditure in Sweden increased, largely due to increased business investment. However, the real growth of R&D expenditure will be modest as inflation impacts the rate of growth.
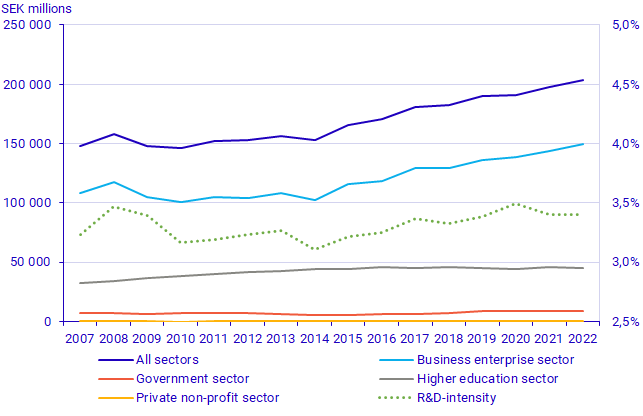
In 2022, total expenditure on intramural R&D amounted to SEK 203,524 million, an increase since 2021 of just under SEK 5.7 billion, or 2.9 percent in 2022 prices. R&D intensity measured as total expenditure on intramural R&D as a share of GDP stood at 3.40%, unchanged since 2021.
Inflation erodes research spending
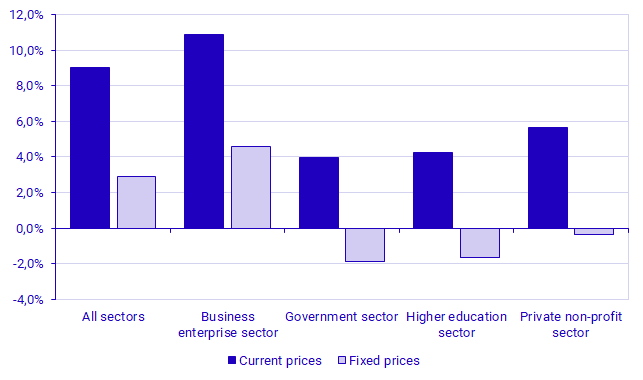
Total expenditure on intramural R&D increased by almost SEK 16.9 billion in current prices between 2021 and 2022, or 9.0 percent. At the same time, growth after adjusting for inflation was only 2.9 percent. The business enterprise sector saw the most growth, growing by 10.9 percent at current prices and 4.6 percent at constant prices. Despite large price changes, business R&D has the strongest real performance since 2019, before the Coronavirus pandemic. The business enterprise sector was also the only sector to show positive growth in real terms. The government sector saw the least growth, with a decrease in real terms of -1.9 percent. Adjustment for inflation is based on GDP and covers the economy as a whole, and it fails to account for the fact that price changes may differ between sectors.
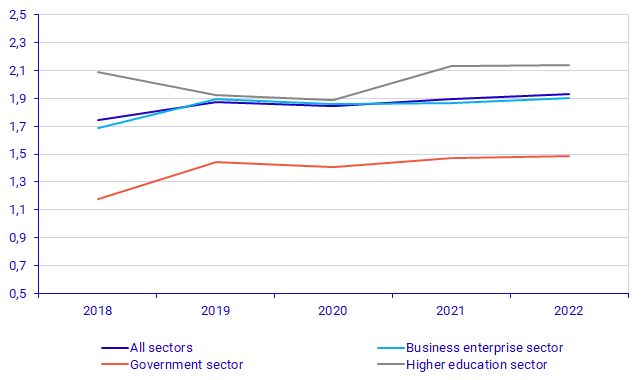
Strong GDP growth reduces R&D intensity
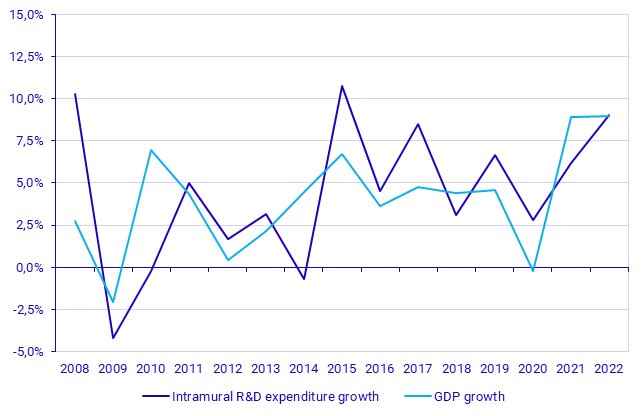
R&D intensity is the total expenditure on intramural R&D as a share of GDP. Thus, if one indicator grows more quickly than the other, such as when growth of R&D expenditure exceeds GDP growth, R&D intensity will increase. Since 2008, the growth rate of R&D expenditure has exceeded that of GDP in ten of the fifteen years. In 2020, GDP developed negatively while R&D expenditure still developed positively. In 2021, GDP recovery exceeded the growth rate of R&D expenditure, resulting in a decrease in R&D intensity. The growth rate of R&D expenditure in 2022 was in line with GDP growth, resulting in an unchanged R&D intensity since 2021 of 3.40%.
Forecasts and results
The business R&D survey is conducted on a biennial, odd-year basis. During the survey period, enterprises provide a forecast of total expenditure on intramural R&D for the current even-numbered year. These data largely form the basis for business expenditure in even-numbered reference years, but not all enterprises provide a forecast. Since reference year 2020, intramural R&D expenditure in the business enterprise sector has been drawn from the Community Innovation Survey, both for enterprises not previously providing a forecast as well as those that did so, but which provide new data in the innovation survey. As innovation survey data are collected after the end of the reference year, their quality is considered superior, since enterprises have information about the whole reference year after its end.
In the 2021 R&D survey, enterprises projected expenditure on intramural R&D in 2022 of SEK 116,370 million. In 2023, in the innovation survey, the same enterprises reported expenditures on intramural R&D performed in 2022 of SEK 111,021 million. This means that enterprises overestimated imminent R&D expenditures by just over SEK 5.3 billion in the information provided in the R&D survey in the first half of 2022.
For reference year 2020, this relationship was inverted. Enterprise forecasts indicated that SEK 80,678 million would be generated in R&D activities, but the result of the innovation survey showed that the same enterprises generated SEK 82,658 million during the first year of the pandemic. This difference of just under SEK 2 billion means that enterprise forecasts underestimated the extent of R&D subsequently carried out in 2020.
The significant differences between intramural R&D in 2020 and 2022 are due to an increase in the number of R&D companies sampled for the innovation survey in 2022, a change made to further improve the quality of intramural R&D data.
| Year | Forecast | Actual | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 116 370 | 111 021 | ‑5 349 |
| 2020 | 80 678 | 82 658 | 1 980 |
Full-time equivalents increased in 2022
In 2022, the number of full-time equivalents (FTE) in R&D activities in Sweden increased by 7.5 percent. Personnel involved in generating new knowledge and developing products, referred to as researchers, made up 85.4 percent of FTEs. The remainder of this work was done by support personnel such as technicians and administrators. In the last five years, the number of FTEs has increased in all sectors, even during the Coronavirus pandemic.
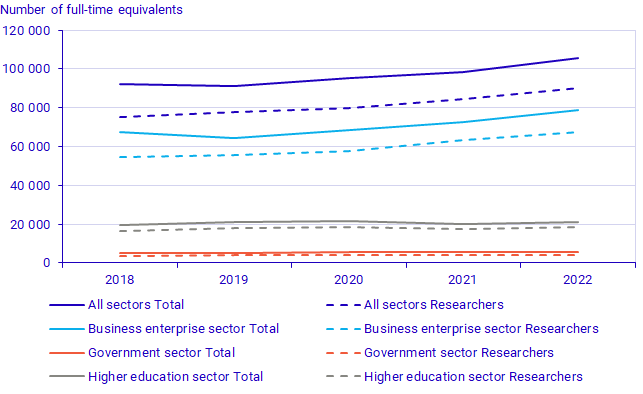
Since 2018, the ratio of R&D expenditure to the number of FTEs generated has remained relatively stable. The indicator itself has an upward trend over time, since inflation and other factors (including necessary investments in capital goods and infrastructure that are greater for some fields of R&D than others) ensure that growth of expenditures exceeds that of working hours. Expenditure per FTE is greatest in the higher education sector (SEK 2.14 million) and least in the government sector (SEK 1.49 million). Business sector expenditure per FTE in 2022 was SEK 1.90 million. In both the business enterprise sector and the higher education sector, expenditure per FTE fell in 2020 and then rose marginally in both 2021 and 2022.
Definitions and explanations
Research and Development (R&D)
Research and experimental development (R&D) comprise creative and systematic work undertaken in order to increase the stock of knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge in all fields of science.
To be defined as R&D, an activity must be:
Novel: An R&D activity undertaken in order to generate new knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge.
Creative:R&D activities based on original concepts or hypotheses.
Uncertain:The final outcome of R&D activities is generally uncertain. There is also uncertainty related to the cost or time needed to achieve the expected results.
Systematic:R&D activities are performed systematically and are planned and budgeted.
Transferable and/or reproducible:An R&D activity should lead to results that could possibly be transferable and/or reproducible.
Intramural R&D
Activities carried out in Sweden by the organisation’s own personnel or by consultants in an R&D project led by the organisation, in the organisation’s own R&D activities. Intramural R&D also includes R&D carried out by commission.
Extramural R&D
R&D activities that the organization has commissioned others to carry out as well as support for R&D that the company has provided to others, for example grants to universities and colleges.
Full-time equivalent in R&D
A full-time equivalent in R&D corresponds to the work a full-time employee performs over one year. A full-time employee who dedicates half their working time to R&D contributes with 0.5 full-time equivalents.
Basic research is experimental or theoretical work undertaken primarily to acquire new knowledge of the underlying foundations of phenomena and observable facts, without any particular application or use in view.
Applied research is original investigation undertaken in order to acquire new knowledge. It is, however, directed primarily towards a specific, practical aim or objective.
Experimental development is systematic work, drawing on knowledge gained from research and practical experience and producing additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new products or processes or to improving existing products or processes.
Private non-profit sector
Intramural R&D expenditures in the private non-profit sector are included in estimated totals. As the sector is relatively small in comparison to other sectors, the statistics are not reported separately. For statistics regarding the private non-profit sector see the Statistical database.
Fixed price calculation
Comparisons over time are presented in the 2021 price level to remove any price effects. For fixed price calculation, a GDP deflator is used.
GDP at market price in nominal and fixed prices is used and published at National-accounts.
R&D intensity is calculated as a percentage of the total intramural R&D expenditure as a share of real GDP.
SNI - Swedish Standard Industrial Classification
For more information, SNI.
The Quality of the statistics
Methodological changes have been implemented for the Higher education sector and the government sector, which affect comparability over time. Among other things, the Swedish Institute of Space Physics is now included in the reporting in the government sector. For further information on the production of the statistics, we refer to our documentation, Statistikens framställning (2022) and Kvalitetsdeklaration (2022). You can find these documents in Swedish at our product page. If you want help interpreting the results you are most welcome to contact us.
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
