Number of full-year persons receiving social assistance and benefits 2018
Number of persons receiving economic support decreased
The number of full-year persons receiving economic support in the form of social assistance or benefits decreased by 4.4 percent in 2018. The total number in 2018 was 772 275 persons, which corresponds to 13.3 percent of the population. There are large differences between different parts of the country. The proportion was lowest in commuting municipalities near large cities, at 9.8 percent, and highest in rural municipalities, at 17.0 percent.
Benefit systems are measured in full-year persons, or full-year equivalents. This allows for comparability between different types of benefits. The term ‘full-year equivalent’ refers to the number of individuals who can be supported during an entire year on full benefits. For example, two persons who have both been unemployed full-time for six months amount to one full-year equivalent.
Statistics Sweden annually reports statistics on the number of full-year persons aged 20–64 who receive economic support in the form of social assistance or benefits, such as sickness benefits, sickness or activity compensation, unemployment benefits, economic aid and introduction benefit.
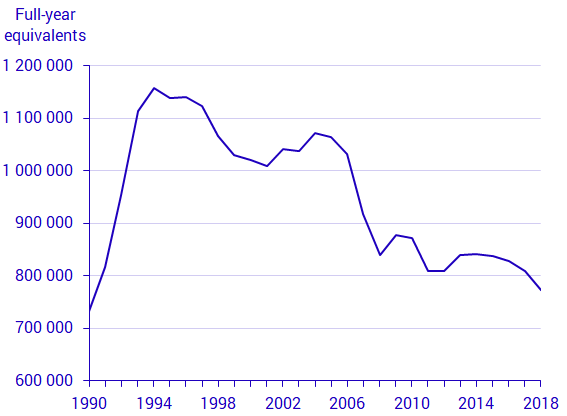
The number of full-time equivalents rose sharply in the early 1990s; between 1990 and 1994, the number rose by almost 60 percent, but has steadily decreased since then. In 2018, the number had declined to almost the same level as in 1990. Between 2017 and 2018, the number decreased in all compensation forms except in unemployment benefits, where it increased by 4.1 percent.
Full-year persons with sickness or activity compensation, who account for about 33 percent of the total number of full-year persons, have decreased in number since 2006. In 2018, this number decreased by 6.1 percent to the lowest level since full-year equivalents reporting started in 1990.
Since 2010, the number of full-year persons with sickness benefits increased steadily. This trend was broken in 2017, and in 2018 the number decreased for the second year in a row.
Major regional differences
The number of full-year persons differs in different parts of the country. In a grouping of municipalities by size and location, on average, the proportion was lowest in commuting municipalities near large cities, at 9.8 percent, and highest in rural municipalities, at 17.0 percent.
Municipality group |
Percentage |
|---|---|
Commuting municipalities near large cities |
9.8 |
Large cities |
12.2 |
Rural municipalities with a visitor industry |
12.6 |
Medium-sized towns |
13.8 |
Commuting municipalities near medium-sized towns |
14.3 |
Small towns |
14.4 |
Commuting municipalities near small towns |
16.4 |
Commuting municipalities with a low commuting rate near medium-sized towns |
16.6 |
Rural municipalities |
17.0 |
In 2018, the proportion decreased in all municipality groups, except in commuting municipalities near small towns. In that group, the proportion increased by 0.2 percentage points.
More women than men
Among the full-year equivalents, 54.0 percent are women and 46.0 percent are men. Women are in the majority with regard to sickness benefit and sickness or activity compensation. In the other forms of compensation, the number of full-time equivalents is relatively evenly divided among the sexes.
| Women | Men | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
Sickness benefits |
64.6 | 35.4 | 100.0 |
Sickness or activity compensation |
56.4 | 43.6 | 100.0 |
Unemployment benefits |
45.6 | 54.4 | 100.0 |
Labour market programmes |
46.8 | 53.2 | 100.0 |
Economic aid |
52.6 | 47.4 | 100.0 |
Introduction benefit |
47.2 | 52.8 | 100.0 |
Total |
54.0 | 46.0 | 100.0 |
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
