Purchasing Power Parities 2018-2020
Swedish households’ Actual Individual Consumption 12 percent above EU average
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2021-12-22 9.30
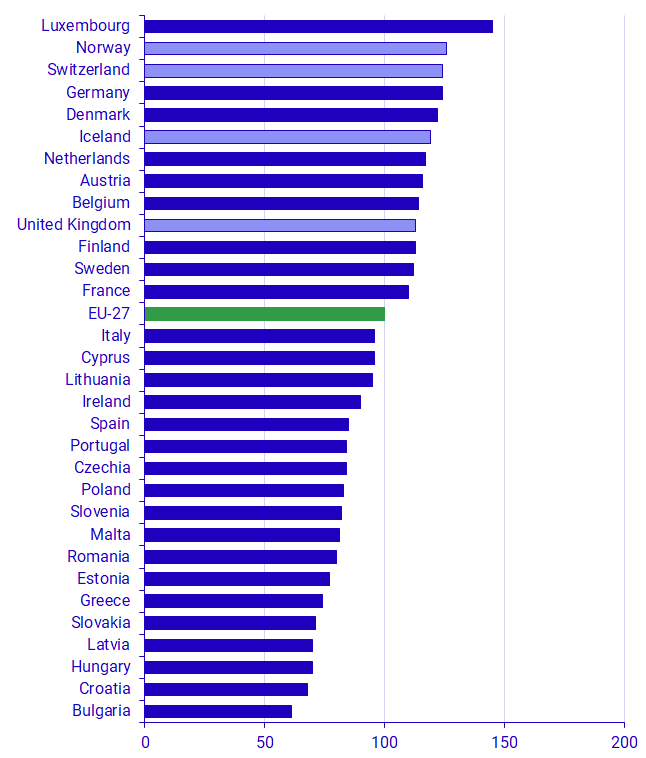
Swedish households’ Actual Individual Consumption (AIC) per capita was 12 percent above the average for the 27 EU countries in 2020.
Source: Eurostat and SCB
AIC per capita varied in 2020 among the 27 EU Member States, Norway, Iceland, Switzerland and the United Kingdom from 45 percent above the EU average to 39 percent below the EU average. Luxembourg tops the list at 45 percent above, followed by Norway, 26 percent above the EU average. However, it should be noted that Norway, Iceland, Switzerland and the United Kingdom are not included in the EU average.
| AIC volume index per capita, EU27=100 | GDP volume index per capita, EU27=100 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| Luxembourg | 152 | 149 | 145 | 262 | 254 | 263 | |
| Norway | 132 | 128 | 126 | 156 | 145 | 140 | |
| Germany | 123 | 122 | 124 | 124 | 121 | 123 | |
| Switzerland | 125 | 123 | 124 | 160 | 157 | 160 | |
| Denmark | 117 | 115 | 122 | 129 | 127 | 135 | |
| Iceland | 116 | 114 | 119 | 128 | 127 | 120 | |
| Netherlands | 115 | 115 | 117 | 129 | 128 | 132 | |
| Austria | 119 | 118 | 116 | 128 | 126 | 124 | |
| Belgium | 114 | 114 | 114 | 118 | 118 | 119 | |
| Finland | 113 | 111 | 113 | 111 | 109 | 113 | |
| United Kingdom | 116 | 117 | 113 | 107 | 107 | 104 | |
| Sweden | 111 | 108 | 112 | 120 | 119 | 123 | |
| France | 109 | 109 | 110 | 104 | 106 | 104 | |
| EU-27 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Cyprus | 95 | 96 | 96 | 91 | 92 | 88 | |
| Italy | 100 | 100 | 96 | 97 | 96 | 94 | |
| Lithuania | 91 | 92 | 95 | 81 | 84 | 87 | |
| Ireland | 95 | 95 | 90 | 190 | 190 | 209 | |
| Spain | 92 | 91 | 85 | 91 | 91 | 84 | |
| Czechia | 84 | 85 | 84 | 92 | 93 | 93 | |
| Portugal | 85 | 86 | 84 | 78 | 79 | 76 | |
| Poland | 78 | 79 | 83 | 71 | 73 | 76 | |
| Slovenia | 81 | 82 | 82 | 87 | 88 | 89 | |
| Malta | 86 | 86 | 81 | 102 | 103 | 97 | |
| Romania | 74 | 78 | 80 | 66 | 69 | 72 | |
| Estonia | 75 | 75 | 77 | 81 | 82 | 84 | |
| Greece | 78 | 77 | 74 | 66 | 66 | 62 | |
| Slovakia | 68 | 69 | 71 | 70 | 69 | 70 | |
| Hungary | 65 | 67 | 70 | 71 | 73 | 74 | |
| Latvia | 71 | 71 | 70 | 69 | 69 | 70 | |
| Croatia | 65 | 66 | 68 | 65 | 66 | 64 | |
| Bulgaria | 57 | 59 | 61 | 52 | 53 | 55 | |
Source: Eurostat and Statistics Sweden Note: The countries are sorted by descending AIC in 2020.
GDP per capita is mainly an indicator of economic activity in a particular country.
In 2020, Sweden’s GDP per capita in PPS was 23 percent above the EU average. Luxembourg had by far the highest GDP per capita, at 163 percent above the EU average. This high figure is due, in part, to the large proportion of foreign workers in the country, who contribute to GDP, but are not included in the population statistics. The lowest figure recorded in this comparison was 45 percent below the EU average, in Bulgaria.
Purchasing power parities (PPP) are currency conversion rates that are applied in order to convert economic indicators from national currency to artificial common currency, called Purchasing Power Standard (PPS), which equalises the purchasing power of different national currencies and enables meaningful volume comparison between countries.
PPP is the ratio between the amount in the countries’ domestic currency that is needed to purchase the same basket of goods and services.
GDP is first calculated in the domestic currency and later converted with an artificial currency, Purchasing Power Standard (PPS). GDP per capita adjusted with purchasing power reflects the difference in volume in real terms between countries.
Actual Individual Consumption (AIC) refers to all goods and services that are actually consumed by individual households. In international comparisons, AIC is often preferred as an indicator of households’ material welfare.
Definitions and explanations
Purchasing power parities (PPP) are currency conversion rates that are applied in order to convert economic indicators from national currency to artificial common currency, called Purchasing Power Standard (PPS), which equalises the purchasing power of different national currencies and enables meaningful volume comparison between countries.
PPP is the ratio between the amount in the countries’ domestic currency that is needed to purchase the same basket of goods and services.
GDP is first calculated in the domestic currency and later converted with an artificial currency, Purchasing Power Standard (PPS). GDP per capita adjusted with purchasing power reflects the difference in volume in real terms between countries
Actual Individual Consumption (AIC) refers to all goods and services that are actually consumed by individual households. In international comparisons, AIC is often preferred as an indicator of households’ material welfare.
Eurostat’s publishing of Purchasing Power Parities
For further information, see Eurostat’s news release on 2021-12-15
Consumption per capita in purchasing power standards in 2020
Next publishing will be
22 December 2022 at 08:00.
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
