Purchasing Power Parities:
Swedish households’ Actual Individual Consumption 10 percent above EU average
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2017-12-18 9.30
Swedish households’ Actual Individual Consumption (AIC) per capita is 10 percent above average for the 28 EU countries in 2016. Sweden ranks tenth in Europe.
Actual Individual Consumption (AIC) consists of goods and services that are consumed by the individual irrespective of whether these goods and services are purchased and paid for by households, by the government or by non-profit organisations. In international comparisons AIC is often seen as the preferable indicator for households’ actual standard of living.
The dispersion in AIC per capita between the 28 EU countries and Norway, Iceland and Switzerland, ranges from 33 percent above to 47 percent below the EU 28 average. Norway tops the list with 33 percent above, followed by Luxembourg which is 32 percent above and Switzerland which is 28 percent above the average. However, it should be noted that Norway, Switzerland and Iceland is not included in the EU 28 average.
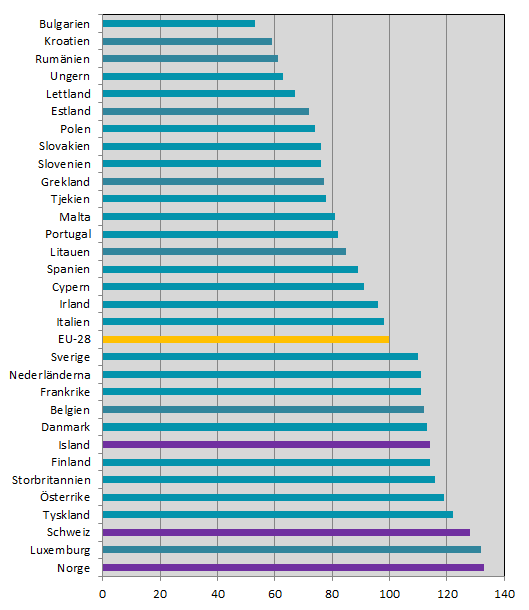
Note: Sorted firstly by value and secondly alphabetically.
GDP per capita is mainly an indicator of the economic activity in a particular country.
Sweden’s GDP per capita is 23 percent above the EU 28 average in 2016. Luxembourg has by far the highest GDP per capita, at 158 percent above the EU average. The relatively high figure is partly due to a large number of foreign residents working in the country and thus contributing to the GDP, while not being included in the population statistics. Bulgaria has the lowest figure in this comparison with 51 percent below the average for the EU countries.
| AIC volume index per capita, EU28=100 | GDP volume index per capita, EU28=100 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
| Norway | 135 | 135 | 133 | 176 | 161 | 148 | |
| Luxembourg | 138 | 135 | 132 | 270 | 267 | 258 | |
| Switzerland | 131 | 131 | 128 | 165 | 166 | 161 | |
| Germany | 124 | 122 | 122 | 126 | 124 | 123 | |
| Austria | 122 | 121 | 119 | 130 | 130 | 128 | |
| United Kingdom | 115 | 115 | 116 | 109 | 108 | 107 | |
| Finland | 114 | 114 | 114 | 111 | 109 | 109 | |
| Iceland | 113 | 112 | 114 | 119 | 123 | 128 | |
| Denmark | 115 | 115 | 113 | 128 | 127 | 124 | |
| Belgium | 115 | 114 | 112 | 119 | 119 | 118 | |
| France | 112 | 111 | 111 | 107 | 105 | 104 | |
| Netherlands | 113 | 112 | 111 | 130 | 129 | 128 | |
| Sweden | 112 | 112 | 110 | 124 | 125 | 123 | |
| EU-28 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Italy | 97 | 97 | 98 | 96 | 95 | 97 | |
| Ireland | 94 | 96 | 96 | 137 | 181 | 183 | |
| Cyprus | 89 | 91 | 91 | 81 | 82 | 83 | |
| Spain | 87 | 89 | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | |
| Lithuania | 81 | 83 | 85 | 75 | 75 | 75 | |
| Portugal | 81 | 82 | 82 | 77 | 77 | 77 | |
| Malta | 79 | 81 | 81 | 90 | 93 | 96 | |
| Czech Republic | 78 | 78 | 78 | 86 | 87 | 88 | |
| Greece | 80 | 79 | 77 | 72 | 69 | 68 | |
| Slovenia | 76 | 76 | 76 | 82 | 82 | 83 | |
| Slovakia | 76 | 76 | 76 | 77 | 77 | 77 | |
| Poland | 74 | 74 | 74 | 67 | 68 | 68 | |
| Estonia | 69 | 71 | 72 | 76 | 75 | 75 | |
| Latvia | 65 | 65 | 67 | 64 | 64 | 65 | |
| Hungary | 62 | 63 | 63 | 68 | 68 | 67 | |
| Romania | 56 | 58 | 61 | 55 | 56 | 58 | |
| Croatia | 59 | 59 | 59 | 59 | 59 | 60 | |
| Bulgaria | 51 | 53 | 53 | 47 | 47 | 49 | |
Source: Eurostat and SCB Source: Eurostat and SCB. Note: Norway, Iceland and Switzerland are not EU-members and are therefore not included in the EU28 average. Sorted firstly by AIC in 2016 and secondly in alphabetical order.
Definitions and explanations
Purchasing power parities (PPP) are currency conversion rates that are applied in order to convert economic indicators from national currency to artificial common currency, called Purchasing Power Standard (PPS), which equalises the purchasing power of different national currencies and enables meaningful volume comparison between countries.
PPP is the ratio between the amount in the countries’ domestic currency that is needed in order to buy the same basket of goods and services.
GDP is first calculated in the domestic currency and later converted with an artificial currency, Purchasing Power Standard (PPS). GDP per capita adjusted with purchasing power reflects the difference in volume in real terms between countries.
Information on Eurostat revision of PPP time series
Eurostat publishes a revised time series of Purchasing Power Parities (PPP), on 13 December. The revision starts from 1995. The revision was undertaken for three main reasons:
• to incorporate the latest national accounts data that was produced under ESA2010 by all Member States and other countries;
• to harmonise, to the maximum extent, the methodology used to calculate the PPPs for all reference years; and
• to introduce, for all reference years, the latest classification of expenditures.
Purchasing Power Parities
Eurostat’s publishing of Purchasing Power Parities
For more informatio, see Eurostat´s newsrelease
The Eurostat website and database
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
