Research and development in Sweden 2023
R&D activity in Sweden grows in 2023
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2024-10-31 8.00
Intramural research and development (R&D) expenditure in Sweden increased by 3 percent, from SEK 216 billion to SEK 224 billion in fixed prices, between 2022 and 2023. R&D personnel also increased compared to the previous year, with 1 percent to a total of about 106 000 full-time equivalents in 2023. Data for 2023 also show that Swedish enterprises spent SEK 14.6 billion on energy related R&D.
During 2023, intramural R&D expenditure in Sweden amounted to SEK 224 billion. This is an increase of 3 percent or about SEK 7.4 billion compared to 2022 in fixed prices. In both the Government sector and the Higher education sector, the increases were small in fixed prises, about 1 percent respectively. The Business enterprise sector saw a more substantial increase of 4 percent compared to 2022. Due to relatively high inflation during 2023, there is a significant difference between fixed and current prices which affects the comparison over time. Measured in current prices, total R&D expenditure increased by 10 percent compared to 2022; 11 percent in the Business enterprise sector and 7 percent in the Government sector and Higher education sector respectively.
The R&D personnel increased by 1 percent compared to 2022, to about 106 000 full-time equivalents in 2023. In the Government sector and the Higher education sector the increase amounted to 3 percent and 4 percent respectively which means that the R&D personnel showed a stronger development than expenditures in these sectors measured in fixed prices. The opposite holds for the Business enterprise sector where R&D personnel remained unchanged compared to 2022. In current prices, R&D expenditure showed a stronger increase than personnel, indicating increased costs for R&D activities.
For a second year, R&D intensity (R&D expenditure as a share of GDP) in Sweden rose. During 2023, the R&D intensity amounted to 3.60 percent, which is an increase by 0.19 percentage points compared with 2022. The increase is partly explained by the increase in R&D expenditure, partly by a decrease in GDP in fixed prices between 2022-2023. In current prices, GDP increased, yet relatively less than R&D expenditure.
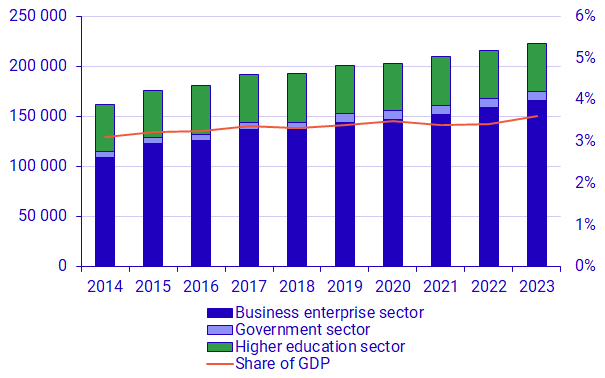
Note 1. Intramural R&D expenditure in the private non-profit sector represent less than 1 percent of total intramural R&D expenditure in Sweden and is therefore excluded from the figure. It is, however, included when calculating R&D intensity.
The Business enterprise sector saw the most significant increase in R&D expenditure, both in relative and in absolute terms. Of the total increase of SEK 7.4 billion between 2022 and 2023, the Business enterprise sector stood for SEK 7.0 billion, which is 94 percent of the increase. For the Business enterprise sector to show a stronger development than that of other sectors is not new for 2023. Over the last nine years, R&D expenditure in the Business enterprise sector have had a stronger upward trend than in the other sectors. This also means that the Business enterprise sector has increased its’ share of total R&D expenditure from 67 percent in 2014 to 74 percent in 2023.
The Business enterprise sector also contributed the majority of funds for intramural R&D. In all, the sector financed 64 percent of all intramural R&D in Sweden during 2023. Almost 99 percent of this funding stayed within the Business enterprise sector, either as self-financing or as funding to other enterprises within or outside the enterprise group. The Government sector follows as the next largest funder of intramural R&D. The majority of funds from the Government sector went to the Higher education sector, primarily as general university funds. In the Higher education sector, a relatively large share of the funds came from the private non-profit sector in 2023, about 14 percent.
|
Source of funds |
Sector |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business enterprise sector |
Government sector |
Higher education sector |
Private non-profit sector |
Total | ||
|
Business enterprise sector
|
140 018 | 640 | 1 366 | 50 | 142 074 | |
|
Government sector
|
7 693 | 8 032 | 33 378 | 177 | 49 280 | |
|
Higher education sector
|
122 | 79 | 2 644 | 57 | 2 901 | |
|
Private non-profit sector
|
95 | 145 | 6 871 | 77 | 7 189 | |
|
Rest of the world
|
18 193 | 291 | 3 629 | 68 | 22 182 | |
|
Total
|
166 121 | 9 188 | 47 888 | 429 | 223 626 | |
Energy related R&D in enterprises primarily focused on energy efficiency
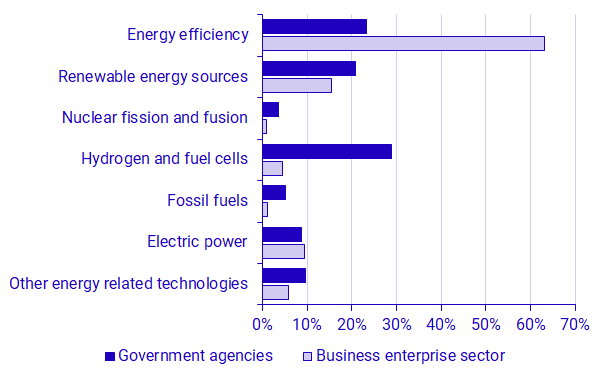
Developing sustainable energy systems is an important aspect of the green transition. For 2023, Statistics Sweden has surveyed energy related R&D. The data captures both funding of energy related R&D provided by government agencies and energy related intramural R&D performed by enterprises.
During 2023, government agencies funded extramural R&D in energy to an amount of SEK 2.4 billion. The funding was primarily directed towards R&D on hydrogen and fuel cells, energy efficiency, and renewable energy sources. These areas amounted to about 73 percent of government agencies’ total extramural R&D expenditure on energy.
In the Business enterprise sector, intramural R&D expenditure on energy amounted to SEK 14.6 billion in 2023. The majority of the expenditure, SEK 9.2 billion, was directed toward R&D on energy efficiency. Hydrogen and fuel cells, which was the area that received most of the funding from the government agencies, constituted only 4 percent of business enterprises’ intramural R&D expenditure on energy. However, these 4 percent correspond to SEK 639 million, compared to government agencies’ extramural R&D expenditure within the same area of SEK 702 million.
The enterprise group was the most important source of funds in the largest R&D industries
The seven industries with the largest R&D expenditures made up 87 percent of total R&D expenditure in the Business enterprise sector with about SEK 144 billion. In all of these seven industries, excepting manufacture of electrical equipment (SNI 27), self-financing was the primary source of R&D funds. Self-financing constituted at least 50 percent of R&D expenditure in five of the seven industries.
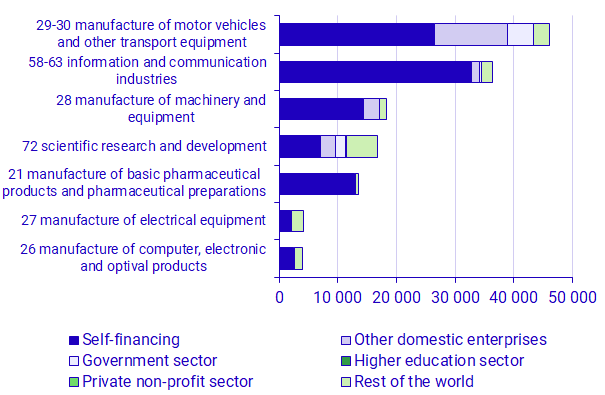
Within the industry for manufacture of electrical equipment, 51 percent of intramural R&D expenditure was funded by foreign sources. A majority of these funds were from other enterprises within the same enterprise group located abroad. Similarly, in the industry for manufacture of motor vehicles and other transport equipment (SNI 29-30) a relatively large share of R&D expenditure was funded by other enterprises in Sweden. This was, almost exclusively, funds from other enterprises in the same enterprise group. Within the industry for manufacture of motor vehicles and other transport equipment, 6 percent of R&D expenditure were funded by foreign sources. In this case, a majority of the funds from the rest of the world came from government units abroad.
Medical and health sciences was the largest field of R&D
Medical and health sciences is the largest field of R&D in both the Higher education sector and the Government sector. During 2023, the higher education institutions’ intramural R&D expenditure on medical and health sciences amounted to SEK 14.5 billion, while the corresponding expenditure in the Government sector was SEK 5.5 billion.
Compared with 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, R&D expenditure on medical and health sciences has increased in current prices both in the Higher education sector and in the Government sector. However, measured in fixed prices this expenditure decreases for the Higher education sector, which could indicate that the capacity to perform R&D within the field has not increased. The most significant increases have instead taken place within the fields of natural sciences and social sciences. Based on an analysis made by the OECD, one of the areas receiving most of the government funding in Sweden in connection to the pandemic was epidemiology and social interventions. This includes R&D on various social aspects of the pandemic such as working from home or the effects of the pandemic on the economy[1], which could, at least partly, explain this development.
[1] Measuring governments’ R&D funding response to COVID-19: An application of the OECD Fundstat infrastructure to the analyses of R&D directionality, OECD. 2023.
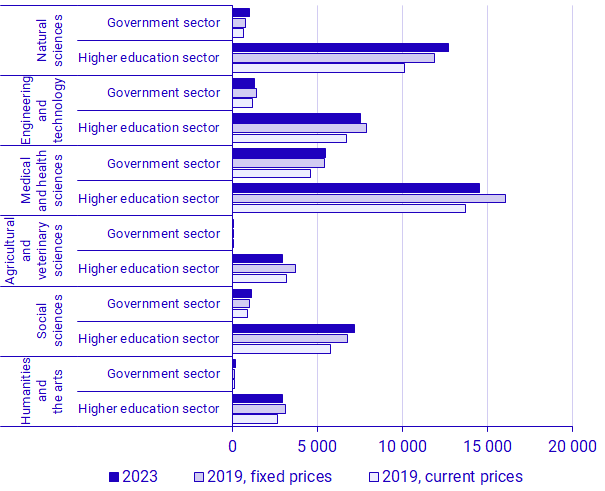
In the Government sector, it is mainly the regions that perform R&D on medical and health sciences. Their R&D expenditure constituted 96 percent of the sector’s expenditure within the field and 57 percent of the sector’s total R&D expenditure. In the other sub-sectors, social sciences is the largest field of R&D, excepting government agencies among which the largest share of R&D expenditure is allocated to engineering and technology.
In the Higher education sector, universities account for most of R&D expenditure, both in general and within medical and health sciences specifically. Of the universities’ total R&D expenditure, 31 percent was allocated to medical and health sciences in 2023. This was also the largest field of R&D among individual education providers, with 57 percent. However, these institutions made up only 0.2 percent of total R&D expenditure in the sector.
Definitions and explanations
Research and Development (R&D)
Research and experimental development (R&D) comprise creative and systematic work undertaken in order to increase the stock of knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge in all fields of science.
To be defined as R&D, an activity must be:
Novel: An R&D activity undertaken in order to generate new knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge.
Creative: R&D activities based on original concepts or hypotheses.
Uncertain: The final outcome of R&D activities is generally uncertain. There is also uncertainty related to the cost or time needed to achieve the expected results.
Systematic: R&D activities are performed systematically and are planned and budgeted.
Transferable and/or reproducible: An R&D activity should lead to results that could possibly be transferable and/or reproducible.
Intramural R&D
Activities carried out in Sweden by the organisation’s own personnel or by consultants in an R&D project led by the organisation, in the organisation’s own R&D activities. Intramural R&D also includes R&D carried out by commission.
Extramural R&D
R&D activities that the organisation has commissioned others to carry out as well as support for R&D that the company has provided to others, for example grants to universities and colleges.
Full-time equivalent in R&D
A full-time equivalent in R&D corresponds to the work a full-time employee performs over one year. A full-time employee who dedicates half their working time to R&D contributes with 0.5 full-time equivalents.
Basic research is experimental or theoretical work undertaken primarily to acquire new knowledge of the underlying foundations of phenomena and observable facts, without any particular application or use in view.
Applied research is original investigation undertaken in order to acquire new knowledge. It is, however, directed primarily towards a specific, practical aim or objective.
Experimental development is systematic work, drawing on knowledge gained from research and practical experience and producing additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new products or processes or to improving existing products or processes.
Private non-profit sector
Intramural R&D expenditures in the private non-profit sector are included in estimated totals. As the sector is relatively small in comparison to other sectors, the statistics are not reported separately. For statistics regarding the private non-profit sector see the Statistical database.
Fixed price calculation
Comparisons over time are presented in the 2023 price level to remove any price effects. For fixed price calculation, a GDP deflator is used. GDP at market price in nominal and fixed prices is used and published at National-accounts.
R&D intensity is calculated as a percentage of the total intramural R&D expenditure as a share of real GDP.
SNI - Swedish Standard Industrial Classification
For more information, SNI.
The Quality of the statistics
Methodological changes have been implemented for the Business sector, the Private non-profit sector and the Government sector, which affect comparability over time. For further information on the production of the statistics, we refer to our documentation, Statistikens framställning (2023) and Kvalitetsdeklaration (2023). You can find these documents in Swedish at our product page. If you want help interpreting the results you are most welcome to contact us.
Next publishing will be
Every year in October, Statistics Sweden publishes statistics regarding R&D expenditure and personnel in Sweden. It is a part of Sweden's official statistics. More detailed analyses of the respective sectors will be published according to the dates below:
- 12 December, the Higher education sector
- 23 January, the Government sector
- 13 February, the Business enterprise sector
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
