Number of full-year persons receiving social assistance and benefits 2022
Number of persons receiving economic support decreased
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2023-03-23 8.00
The number of full-year persons receiving economic support in the form of social assistance and benefits decreased by 9.7 percent in 2022. The total number in 2022 was 708 249 people, which corresponds to 11.9 percent of the population of working age. This share was lowest in commuter municipalities close to a large town, at 9.3 percent, and highest in Low-commuter municipality close to a medium-sized town and commuter municipalities close to a small town, at 14.5 percent.
Statistics Sweden annually reports statistics on the number of full-year persons aged 20–64 who receive economic support in the form of social assistance and benefits. These comprise sickness benefits, sickness or activity compensation, unemployment benefits, labour market policy measures, economic aid, and introduction benefit.
Different types of benefits can be made comparable by using ‘full-year equivalents’, that shows how many individuals could be supported during an entire year on full benefits. For example, two persons who have both been unemployed full-time for six months together amount to one full-year equivalent.
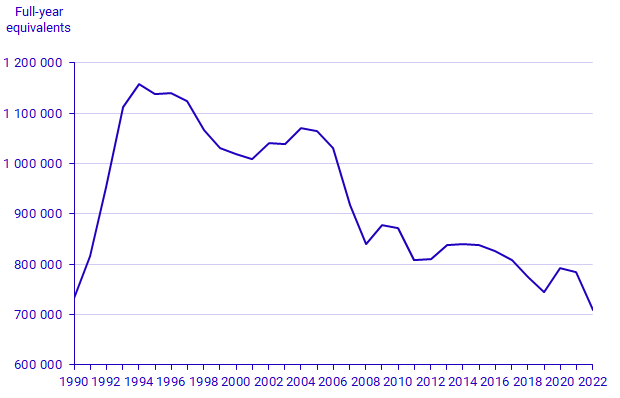
The number of full-year equivalents receiving social assistance and benefits rose by almost 60 percent between 1990 and 1994. Since then, the figure has dropped steadily, and in 2019 it was almost at the same level as in 1990. Between 2019 and 2020, the number of full-year equivalents increased but between 2020 and 2021, the number of full-year equivalents decreased again. In 2022, the number of full-year equivalents was at the lowest level since measurements began in 1990. In 2022, unemployment benefits, economic aid, labour market programmes, sickness or activity compensation and introduction benefit were the forms of compensation that decreased, while sickness benefits increased.
Sickness and activity compensation, which is the largest form of compensation and accounted for about 29.5 percent of the total number of full-year equivalents, has decreased since 2006. In 2022, this form decreased by 3.7 percent and has thus decreased by 54 percent since 2006.
Introduction benefit was introduced in 2011 and the number of full-year equivalents for this form of compensation increased sharply until 2017. However, in the last years this number has decreased sharply; in 2022 it decreased by 27.4 percent
The form of compensation that contributed most to the reduction in the number of full-year equivalents in 2022 was unemployment benefits, which decreased by 33.5 percent.
Major regional differences
The proportion of full-year equivalents who received social assistance and benefits varies across the country. Among the population aged 20–64 years, the proportion of people who received social assistance was lowest in Stockholm County at 9.4 percent and highest in Gävleborg County at 16.3 percent. The difference between these counties was largest among the share of the population in labour market policy measures; In Stockholm County this proportion was 2.4 percent, while in Gävleborg County it was 5.2 percent. Between 2021 and 2022, the proportion of full-year equivalents decreased in all counties.
At the municipal level, the differences were even greater. In 2022, the proportion of full-year equivalents was lowest in Danderyd at 5.4 percent and highest in Filipstad and Söderhamn at 20.3 percent.
| Lowest share | Highest share | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danderyd | 5.4 | Filipstad | 20.3 | |
| Vellinge | 5.9 | Söderhamn | 20.3 | |
| Lomma | 6.3 | Perstorp | 20.2 | |
| Solna | 6.3 | Flen | 19.6 | |
| Täby | 6.4 | Ljusnarsberg | 18.8 | |
| Lidingö | 6.5 | Åmål | 18.6 | |
| Nacka | 6.6 | Degerfors | 18.5 | |
| Vaxholm | 7.4 | Lessebo | 18.4 | |
| Kungsbacka | 7.5 | Fagersta | 18.4 | |
| Knivsta | 7.5 | Bollnäs | 18.1 | |
In a classification based on size and location of the municipality (according to SALAR’s municipality group classification), the proportion of people who received social assistance and benefits was on average lowest in commuter municipalities close to a large city at 9.3 percent, and highest in Low-commuter municipality close to a medium-sized town and commuter municipalities close to a small town at 14.5 percent. Between 2021 and 2022, this proportion decreased in all municipal groups.
| Municipality group | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Commuter municipality close to a large town | 9.3 |
| Rural municipalities with a visitor industry | 11.0 |
| Large cities | 11.0 |
| Medium-sized towns | 12.5 |
| Commuter municipality close to a medium-sized town | 12.7 |
| Small towns | 12.8 |
| Rural municipalities | 14.4 |
| Low-commuter municipality close to a medium-sized town | 14.5 |
| Commuter municipality close to a small locality | 14.5 |
More women than men
Among the full-year equivalents in 2022, 54.8 percent were women and 45.2 percent were men. The distribution between women and men has been roughly unchanged since 2006 when the information was first reported broken down by sex. Women are in a clear majority in the compensation form sickness benefit. Unemployment benefits are the only form of compensation for which there are more men than women.
| Women | Men | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sickness benefits | 63.6 | 36.4 | 100.0 |
| Sickness or activity compensation | 55.3 | 44.7 | 100.0 |
| Unemployment benefits | 45.5 | 54.5 | 100.0 |
| Labour market programmes | 50.5 | 49.5 | 100.0 |
| Economic aid | 53.2 | 46.8 | 100.0 |
| Introduction benefit | 56.7 | 43.3 | 100.0 |
| Total | 54.8 | 45.2 | 100.0 |
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
